Good Posture for a Healthy Back
Overview
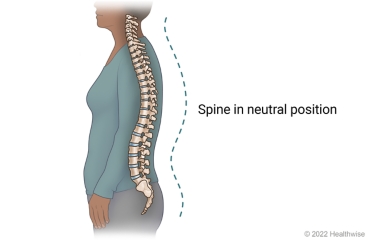
Good posture helps protect your back when you sit, stand, and walk. Good posture means your ears, shoulders, and hips are in a straight line, with your spine in three front-to-back curves that give it an "S" shape. These curves help absorb stress and impact on your back.
Sitting with good posture
To protect your back, pay attention to your posture when you sit.
- Keep your back straight when sitting down.
Use your arms on the arms or seat of the chair to lower yourself.
- Sit with your hips and knees at about the same level. Support your lower back.
- Sit in a chair that is low enough to let you place both feet flat on the floor with both knees nearly level with your hips.
- If your chair or desk is too high, use a footrest to raise your knees.
- Keep your shoulders back and down, your chin back, your belly in, and your lower back supported.
- Place a small pillow, a rolled-up towel, or a lumbar roll in the curve of your back if you need extra support.
- Try different chairs.
Find one that's comfortable for you.
- When driving, adjust your seat to support your back.
- Before you drive, adjust your seat so that your knees are nearly level with your hips.
- Sit straight, and drive with both hands on the steering wheel. Your arms should be in a slightly bent position.
- If your seat angles down from front to back, create a more horizontal surface to sit on with a travel cushion or triangular foam wedge.
Do not sit for long periods. Take regular breaks to walk around and stretch.
Standing with good posture
The following tips may help you have good posture when you are standing.
- Keep your ear, shoulder, hip, and ankle in a line.
- Avoid locking your knees while standing.
Try placing one foot on a low stool if you must stand in one position for a long time, such as when you wash dishes or do other tasks. Switch feet every few minutes.
- Keep your lower back in the neutral position.
A healthy back has three natural front-to-back curves that give the spine an "S" shape. Too much curve (swayback) or too little curve (flat back) can cause problems. The right amount of curve is called the neutral position.
Walking with good posture
Walking is one of the best things you can do for your back. You may find that your back hurts less when you walk. But if you're concerned about any back pain you have while walking, talk to your doctor.
- Keep good posture as you walk.
This generally means that your ears, shoulders, and hips are in a straight line.
- Keep your head up and your eyes forward.
- Every once in a while, shrug your shoulders and then relax them.
This will remind you not to keep your shoulders tense as you walk.
Comfortable sleeping positions
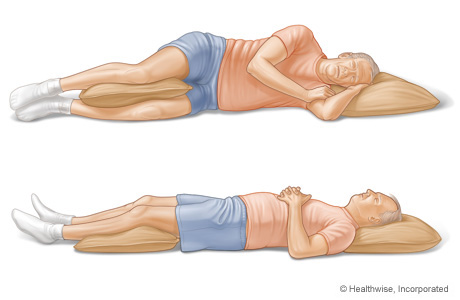
To be more comfortable while you sleep, support your body so that you don't twist your back.
- If you sleep on your side, place a pillow between your knees. This keeps your top leg from falling over your bottom leg and twisting your back. You also can put a small, rolled-up towel under your waist.
- If you sleep on your back, place a pillow under your knees. You also can put a small, rolled-up towel under the curve of your back.
Many people find that these sleeping positions work for them, but they may not work for you. Find the position that helps you the most. If you have a very soft mattress, you may find that switching to a firmer one is more comfortable for your back.
Credits
Current as of: July 17, 2023
Author: Healthwise Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.
Current as of: July 17, 2023
Author: Healthwise Staff
Clinical Review Board
All Healthwise education is reviewed by a team that includes physicians, nurses, advanced practitioners, registered dieticians, and other healthcare professionals.