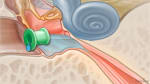
Overview
Tympanometry tests the movement of the eardrum when an ear infection or other middle ear problem is suspected. A doctor places the tip of a handheld tool into the child's ear. The tool changes the air pressure inside the ear and produces a clear tone. Then the tool measures how the eardrum responds to the pressure and the sound. The results of this test are used to help figure out what is going on in the ear.
Why It Is Done
The results of tympanometry can tell doctors whether there is fluid behind the eardrum or whether an ear tube is blocked. The test can also discover whether there is a hole in the eardrum. This information helps doctors decide what kind of treatment your child may need.
Results
Normally the eardrum moves easily when pressure in the ear canal is changed. Most of the time, if the test is normal, there is no fluid behind the eardrum.
An abnormal test result may mean that there is fluid behind the eardrum. It can also mean that the eustachian tube, which connects the back of the nose and throat with the middle ear, is not working well.
Credits
Current as of: October 3, 2025
Current as of: October 3, 2025